AWS KMS supports AWS CloudTrail, a service that logs AWS API calls and related events for your AWS account and delivers them to an Amazon S3 bucket that you specify. By using the information collected by CloudTrail, you can determine what requests were made to AWS KMS, who made the request, when it was made, and so on.
Cloud security refers to a set of policies, technologies or controls that are used to protect data, applications and associated infrastructure. Organizations want their deployed resources and workload to be safe from any potential security threat. AWS KMS (Key Management Service) provides security in terms of encryption to your cloud resources in AWS.
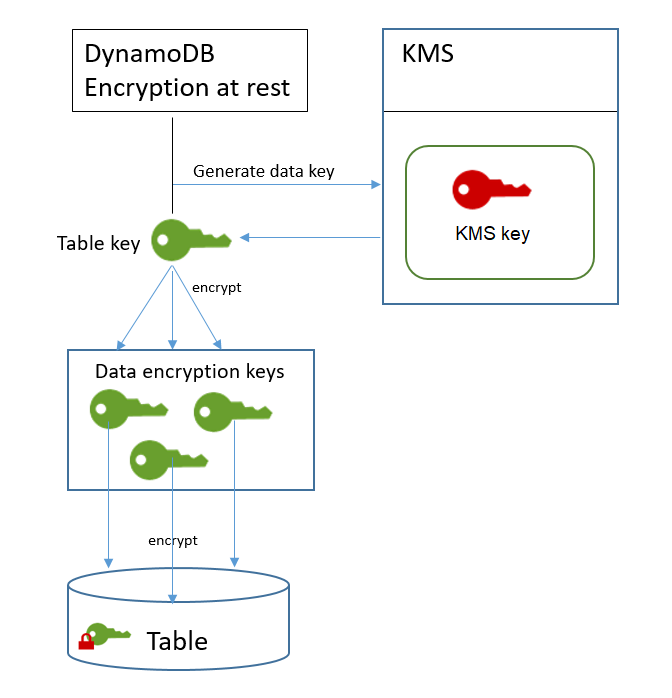
What is Key Management Service (KMS)?
AWS KMS supports symmetric and asymmetric CMKs. A symmetric CMK represents a 256-bit key that is used for encryption and decryption. An asymmetric CMK represents an RSA key pair that is used for encryption and decryption or signing and verification (but not both), or an elliptic curve (ECC) key pair that is used for signing and verification. Setting up the AWS KMS. Contributors Download PDF of this page. If you want to use Amazon encryption with Cloud Volumes ONTAP, then you need to set up the AWS Key Management Service (KMS). Ensure that an active Customer Master Key (CMK) exists.
AWS KMS (Key Management Service) is an encryption service provided by AWS that enables the user to easily encrypt their data. KMS provides a key storage management solution so that data can be encrypted across AWS services and resources within a single AWS account. The easiest method to get started on KMS is to check off the box to encrypt your data within supported AWS services. In this case, default keys created by AWS in user’s account are used. KMS also allows users to create their own keys or CMKs (Customer Master Keys) to have further control over the management of their AWS resources. KMS assigns keys to be used in supported services of AWS when creating encrypted resources and also allows to use them directly within existing applications. It also gives the provision of usage policies to configure which user can use which key to encrypt or decrypt data.
Why KMS key rotation is necessary for AWS users?
Aws Kms Cli
The best cryptographic practices do not encourage excessive use of old CMK. It is highly recommended to rotate your CMK’s to ensure the security of your cloud infrastructure. When automatic key rotation is enabled, KMS generates new cryptographic material every 365 days and retains the older cryptographic material (old key). In this way, both keys can be used to encrypt or decrypt data. There are various benefits of enabling automatic rotation of CMK. Properties of CMK’s such as key ID, key ARN, policies, permissions do not change. It is not required by the user to remember any schedule or calendar to update CMK.
How does Centilytics assist you in ensuring security through KMS?
Centilytics recommends focusing on timely rotation and management of keys to ensure higher security levels of your cloud environment. A dedicated insight is provided which on KMS key rotation checks whether key rotation for your AWS account is enabled or not.
Insight descriptions
There can be 2 possible scenarios:
| Severity | Description |
| OK | This indication will be shown when key rotation is enabled for the corresponding CMK created by AWS user i.e. CMK will be rotated automatically in 365 days by AWS. |
| CRITICAL | This indication will be shown when key rotation is disabled for the corresponding CMK created by AWS user i.e. CMK will not be rotated automatically by AWS. |
Description of further columns are as follows:
- Account Id: This column shows the respective account ID of the user’s account.
- Account Name: This column shows the corresponding account name to the user’s account.
- Identifier: This column shows the unique CMK ID or key ID to uniquely identify and differentiate different keys in AWS.
- Key Rotation Status: This column shows the key rotation status of the corresponding AWS account. If the key rotation is active, then enabled will be displayed. Otherwise disabled will be displayed.
Compliances covered:
| Compliance Name | Reference No. | Link |
| PCI | 3.6.4,3.6.5 | https://docs.aws.amazon.com/quickstart/ latest/compliance-pci/welcome.html |
| HIPAA | 164.312(d),164.312(e)(i) | https://aws.amazon.com/quickstart/ architecture/compliance-hipaa/ |
| ISO 27001 | A.12.4.1, A.12.4.3 | https://www.iso.org/standard/54534.html |
| NIST 800-53 | SC-12, SC-13,SC-17,SC-28 | https://docs.aws.amazon.com/quickstart/ latest/compliance-nist/welcome.html |
| GDPR | Article 30 | https://gdpr-info.eu/ |
Filters applicable:
| Filter Name | Description |
| Account Id | Applying account Id filter will display data for the selected account Id. |
| Severity | Applying severity filter will display data according to the selected severity type i.e. selecting critical will display all resources with critical severity. Same will be the case for warning and ok severity types |
| Resource Tags | Applying resource tags filter will display those resources which have been assigned the selected resource tag. For e.g.- If the user has tagged some resource by a tag named environment, then selecting an environment from the resource tags filter will display all the data accordingly. |
| Resource Tags Value | Applying resource tags value filter will display data which will have the selected resource tag value. For e.g.- If the user has tagged some resource by a tag named environment and has given it a value say production (environment: production), then the user will be able to view data of all the resources which are tagged as “environment:production”. User can use the tag value filter only when a tag name has been provided. |
Read more:
[1] https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/rotate-keys.html
[2] https://aws.amazon.com/kms/faqs/
March 12, 2021
AWS KMS is an incredible offering by AWS that manages encryptionkeys, automatic rotation and secure storage. With rotation enabled,AWS will generate a new encryption key once a year without deletingthe previous keys. Any cipher generated by old keys can still bedecrypted. We don’t have access to the actual key, which meanswe can’t leak it.
Laravel ships an Encrypter class that uses AES for encryption.Replacing Laravel’s implementation with KMS takes only a simpleKmsEncrypter and a Service Provider.
The Service Provider

I just sent out a pull request to introduce a StringEncrypterinterface into Laravel so that this process can be simplified.https://github.com/laravel/framework/pull/36578
The Service Provider can look like this:
Notice how we’re instantiating a KmsClient inside the KmsEncrypterfactory callback. That gives us the chance of delegating howwe should resolve KmsClient to a separate process. One wayof doing that could be like this:
KmsEncrypter
Here’s how KmsEncrypter would look like:
Let’s dissect this class. First we have the KmsClient thatalready carries every configuration necessary to interactwith AWS KMS. Whether you use environment variable with AWSCredentials or let your AWS service assume role with permissionto interact with KMS, AWS SDK will handle the authentication.Then we have the key which should be the ARN of the AWS KMS keyor Alias of the key to be used. Finally we have context. Contextis a non-secret information (e.g. it will be plain text on CloudTrail)that allows you to bind your encryption with a specific signingcontext. If the exact same context is not provided when tryingto decrypt a specific cipher text, then the decryption will notwork. For instance, you may choose to use your service name asthe context of your encryption so that if other services accidentallytries to decrypt your cipher texts, it won’t just work. The developerwould have to make a conscious decision to specify another service’scontext when trying to decrypt cross-service data.
For ease of use, we can base64_encode() the cipher text and thenbase64_decode before decryption so that it’s easier to passthe data around. If you’re interested in learning more aboutbase64_encode, check out my post on Should I encrypt, hash or encode?.
Aws Kms Security Best Practices
Eloquent
Since the ServiceProvider is replacing the binding behind encrypteron Laravel’s service provider, we’re free to use Eloquent’scast feature to encrypt/decrypt attributes automatically.
This way whenever we try to save something into the password orclient_secret attributes, Eloquent will use KmsEncrypter toencrypt the data being stored and when we’re accessing the attribute,Eloquent Mutators will kick in and decrypt it.
Tests
For my automation tests, I decided to use a NullEncrypter implementationso that I don’t need to integrate directly with AWS KMS to runtests. Here’s how a NullEncrypter could look like:
On test could, we could then replace the binding like this:
Watch out for your storage service
During the development of this implementation, I first wrote a produtfeature without encryption and handed the APIs over to the frontendteam so that they could get started. I then started implementingAWS KMS encryption. I noticed that anytime my code would try todecrypt a cipher text, it would throw an exception saying
The reason I was getting this error was not because of the keynor the context. It was actually because I was interacting witha legacy database with strict=false and a password field oftype varchar(191). What would then happen was that the cipher textwould go above 191 characters and MySQL would truncate the datadown to 191 characters. Losing part of a cipher text means thatwe did not guarantee the integrity of the message and we canno longer decrypt it. Increasing the field size mitigated theissue.
Why don’t we inform the key to the decrypt API call to AWS?
When AWS encrypts a payload, it puts inside the cipher text anidentifier for which key was used for encryption. That way evenif we don’t know which key was used for encryption, AWS can stilldecrypt it as long as you have the complete cipher text and thecontext. This probably facilitates AWS’s job when rotating keys.When the key reaches 1 year of life, AWS will generate a brand newone and start using it for any new encryption. It won’t get ridof the old key, though. So if you make an API call asking fordecryption with a cipher text older than 1 year, AWS can stillfind the identifier for the key used and decrypt it.
Defining a Key with CloudFormation
The following template defines a MyEncryptionKey resource anda MyEncryptionKeyAlias resource. It will also output the aliasalongside the Key ARN. The Key ARN can be used to attach to an IAMRole that will need kms:Encrypt* and kms:Decrypt*. The Aliascan be used as an Environment Variable for your compute resourceso that it can be accessed by Laravel and injected into theKmsEncrypter class.
Conclusion
AWS KMS offering is great for the enterprise world. We will neverleak keys, they will be rotated automatically and it costs penniesfor the benefit that they bring. Laravel’s Encrypter and StringEncrypterinterfaces makes it easy to swap the implementation and offer agreat DX to work with encryption be it directly or via Eloquent.All in all it’s a great service, easy to use and designed to offersafety.
Aws Kms Documentation
It’s important to note that I’m not rolling my own encryption here.I’m swapping Laravel’s Encrypter class with one that uses AWS KMS.In other words, AWS KMS is responsible for encryption/decryptionof the data and we should never roll our own encryption algorithms.
Follow me on Twitter tostay tuned with my latest work.

Aws Kms Pricing
Cheers.
Aws Kms
Marco Aurélio Deleu
Writing bad code for 10 years. Passionate about Laravel and AWS.
